Special Issues
Call for Papers
- Special Issue on AI-Enabled Security at the Edge. Guest Editors: Malka N. Halgamuge, RMIT University, Australia; Dipankar Dasgupta, The University of Memphis, USA; Alireza Jolfaei, Flinders University, Australia; Chia-Feng Juang, National Chung Hsing University, Taiwan. Submissions close 31st of January 2024.
Previously Approved Special Issues
- Special Issue on Conversational AI. Guest Editors: Amir Hussain - Edinburgh Napier University, UK; Oliver Lemon - Heriot-Watt University, UK; Roberto Pieraccini - (formerly) Google NYC, USA; Dong Yu - Tencent AI Lab, USA. Submissions close 1st of October 2023.
- Special Issue on Responsible AI Engineering. Guest Editors: Qinghua Lu - CSIRO, Australia; Apostol Vassilev - NIST, USA; Jun Zhu - Tsinghua University, China; and Foutse Khomh - Polytechnique Montreal, Canada. Submissions close 1st of October 2023.
- Special Issue on AutoML for Non-Stationary Data. Guest Editors: Ran Cheng - Southern University of Science and Technology, China; Hugo Jair Escalante - National Institute of Astrophysics, Optics and Electronics, Mexico; Jan N. van Rijn - Leiden University, Netherlands; Wei-Wei Tu - 4Paradigm Inc., China; Shuo Wang - University of Birmingham, UK; Yun Yang - Yunnan University, China. Submissions closed 23rd June 2023.
- Special Issue on Physics-Informed Machine Learning. Guest Editors: Francesco Piccialli – University of Naples Federico II, Italy, Maizar Raissi - University of Colorado Boulder, USA, Felipe A.C. Viana – University of Central Florida, USA, Giancarlo Fortino – University of Calabria, Italy, Huimin LU - Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan, Amir Hussain - School of Computing, Edinburgh Napier University, Scotland. Submissions closed 30th June 2022
- Special Issue on New Developments in Explainable and Interpretable AI. Guest Editors: K.P. (Suba) Subbalakshmi, Stevens Institute of Technology, USA, Wojciech Samek, Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute HHI, Germany, Xia “Ben” Hu, Rice University, USA. Submissions closed 1st June 2022.
- Special Issue on AI Methods for Maintenance and Safety of Automation Systems. Guest Editors: Bin Jiang, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, Hao Luo, Harbin Institute of Technology, China, Hongtian Chen, University of Alberta, Canada, Nishchal K. Verma, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, India. Submissions Closed: 1st of December 2021.
- Special Issue on Artificial Intelligence Ethics: Technical Solutions and Datadriven Guidelines. Guest Editors: Francesca Rossi - T.J. Watson IBM Research Lab, USA, Keeley Crockett - Manchester Metropolitan University, UK, Lirong Xia - ARensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI), USA, Matt Garratt -, UNSW Canberra, Australia. Submissions Closed: 31st July, 2021.
- Special Issue on Security and Privacy in Machine Learning. Guest Editors: Wenjian Luo, Harbin Institute of Technology, China, Yaochu Jin, University of Surrey, UK, Catherine Huang, McAfee LLC, USA. Submissions Closed: 15th July 2021.
- Special Issue on Sentiment Analysis as a Multidisciplinary Research Area. Guest Editors: Erik Cambria, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Frank Xing, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Mike Thelwall, University of Wolverhampton, UK, Roy Welsch, MIT Sloan School of Management, USA. Submissions Closed: 1st March 2021.
Guidelines for Proposals to the IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence
Scope
The IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence (TAI) is a multidisciplinary journal publishing papers on theories and methodologies of Artificial Intelligence. Applications of Artificial Intelligence are also considered.
Topics covered by IEEE TAI include, but not limited to, Agent-based Systems, Augmented Intelligence, Autonomic Computing, Constraint Systems, Explainable AI, Knowledge-Based Systems, Learning Theories, Planning, Reasoning, Search, Natural Language Processing, and Applications. Technical papers addressing contemporary topics in AI such as Ethics and Social Implications are welcomed.
Editor-in-Chief email:
Aims for Special Issues
A special issue needs to have a theme, and is normally addressing either a topic of significant impact (a hot topic), or a topic that has seen sparse publications and there is a value in overcoming the scattered nature of that literature by having a focus and concentrated special issue.
A special issue brings together the state-of-the-art in a particular niche area in artificial intelligence under the roof of one issue in the journal. The thematic nature of a special issue aims to serve as a collection of papers in a single issue for researchers to read and consult.
A special issue that is focusing on a topic, including applications, need to establish the case that this topic is of high significance to the AI community, of high demand, or both. A special issue on a contemporary topic needs to demonstrate the wide range of research in the area to attract a large number of submissions.
How to propose a special issue?
Commence your planning for a special issue by identifying a topic with an appropriate scope. A special issue on Artificial Intelligence will not be accepted as it is too general. A special issue on A* for 3-SAT is likely to be rejected as it is too specific. A special issue on Approximation Algorithms for Satisfiability, Explainable Neural Networks, or Learning Algorithms for Autonomous Vehicles, strikes the right balance. IEEE TAI is a technical journal. A special issue on the ethical and/or social implications of a branch of AI would need to approach the topic with a technical lens.
Once the guest editors have been identified, you will need to develop a proposal with the following contents:
- Title: be specific in the title and reflect the theme of the special issue. The title is the starting point for people to understand the scope of the special issue
- Description: Explain the motivation for the special issue, the state of the art, and the scope.
- List of topics: List an example of the sub-topics that fall under the scope described above. Avoid being too prescriptive.
- Identify 2-3 leading scientists in this area of research who could write an invited position paper in the area of the special issue. Invitations for invited papers can only be issued by the Editor-in-Chief, and these papers will go through the normal review process of IEEE TAI.
- Timeline: present a reasonable timeline for publication. This is normally 3-4 months to advertise for the special issue, 6-8 weeks to complete first round of review, 4 weeks to allow for authors revision (notice IEEE TAI allows 2 weeks for Minor Revision and 4 weeks for Major Revision. Papers expected to take longer to be revised, a reject and resubmit decision or a final reject decision will be recommended.), 6-8 weeks for a second round of review, and two weeks for authors to submit the final file. From this example, a reasonable time line between the acceptance of a special issue and the acceptance of papers for the special issue is expected to be around 40 weeks. In very special circumstances, this timeframe may become much shorter for topics with significant interest to the community.
- List of Guest Editors: Names, Affiliations, Email Addresses, Websites, Scholar.Google Web Address (optional), Short Bio, and the top 5 papers for each guest editor in the area of the special issue. It is a requirement that one of the Associate Editors for IEEE TAI is one of the guest co-editor. The Associate Editor from TAI will be the associate editor handling the submissions for the special issue. At least one of the remaining guest editors should be an internationally recognised leader in the theme of the special issue. A minimum of two guest editors is needed to propose a special issue to mitigate the risk that one of them becomes unavailable. It also distributes the load on guest editors, while bringing their collective experience to promote and manage a high quality special issue.The total number of guest editors should not exceed four including the Associate Editor from TAI. IEEE TAI encourages diversity in the guest editors, including geographic and inclusion of women and other underrepresented groups as guest editors.
- List of potential authors, their affiliation, and Scholar.Google link (optional)
- A Conflict of Interest Statement: guest editors should declare any conflict of interest arising from proposing a special issue such as the organizations funding any of the guest editors on research on the topic, organizations collaborating with the guest editors on the specific topic, or individuals in close collaboration with any of the guest editors and intend to submit to the special issue. If the special issue is accepted, the Editor-in-Chief will discuss risk mitigation strategies with the guest editors to avoid conflict of interest.
Things to avoid when proposing a special issue
- Avoid proposing a topic outside the scope of IEEE TAI
- Avoid proposing a special issue based on a conference or a special session in a conference. Special issues in IEEE TAI needs to be advertised using an open call to allow anyone working in the area to submit a relevant paper
- Guest editors should avoid submitting papers to their special issue. If they do, their papers will be handled as normal submission to TAI and will only appear in the special issue if they get accepted on time for the special issue.
Submission of a Proposal for a Special Issue
Please forward your proposal to the Editor-in-Chief at ieee.tai.eic@gmail.com.
Approval Decision on Special Issues
IEEE TAI has six issues per year. As such, the bar is very high for accepting a special issue. Once a proposal is submitted for a special issue, the EiC will consult with the Editorial Board. The criteria for acceptance of a special issue revolve around the relevance of the topic to IEEE TAI, the suitability of the topic to attract interest from a wider range of readership in the journal, the technical merit of the proposal, and the alignment of the proposal with the aims of a special issue as being outlined in the aims section above.
Based on comments from the Editorial Board, one of three decisions will be communicated to the proposers of the special issue: (1) the proposal is declined (2) The editorial board suggested changes that need to be considered before re-evaluation of the proposal (3) the proposal is accepted.
Post-Approval of a Special Issue Proposal
If the proposal for a special issue is accepted, the guest editors will need to convert the contents of the proposal to an appropriate call for papers. The call for papers need to be consistent with the proposal. Changes would entail that the decision on the special issue is retracted by the journal. Once the Editor-in-Chief approves the Call for Papers, it will be placed on the journal website under the Special Issue section. Only then the proposers are allowed to advertise for the special issue. It is the responsibility of proposers to advertise for a special issue. It is advisable that the call for papers is sent to all newsletters for the five sponsoring societies, and at minimum to IEEE CIS Newsletter.
Review of Papers in the Special Issue
The review process for papers submitted to a special issue will follow the same standards as a normal submission to the journal. A guest editor could be assigned as a reviewer, except the Associate Editor handling the papers. If a guest editor acts as a reviewer, a minimum of two extra reviewers need to be completed for each paper. The guest editor review could be used to provide a uniform feedback on paper alignment with the theme of the special issue and editorial comments.
The final decision on acceptance of manuscripts in a special issue is made by the Editor-in-Chief of IEEE TAI.
Preparation of the publication of the Special Issue
Once a decision is made on which papers to accept in a special issue, the guest editors should prepare a preface for the special issue. The preface should not exceed two pages using the same template for normal papers in the transactions. The preface should be proof read by a professional proof reader before it gets submitted to the Editor-in-Chief for processing. The Editor-in-Chief will either accept, suggestion modifications to, or reject the preface. While the latter decision is not expected, a preface should only focus on the scientific essence of the special issue, be evidence-based and avoid sitting private agendas or non-scientific speculations. The Editor-in-Chief will communicate with the guest editors to ensure the appropriateness of the preface. However, in situations where this discussion is taking a longer time than the production schedule of the special issue or when an agreement can’t be reached, the preface will not proceed to production.
Review Process
IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence
TAI
Paper Handling Process
For a detailed discussion on the review process and rules for IEEE publications, please refer to the IEEE Publication Services and Products Board Operations Manual (https://pspb.ieee.org/images/files/files/opsmanual.pdf). The current document offers a quick guide to the paper handling process for authors to consider when writing their manuscript, and for reviewers to use as a guide to provide their review.
The formal scope for TAI is
The IEEE Transactions on artificial intelligence (TAI) is a multidisciplinary journal publishing papers on theories and methodologies of Artificial Intelligence. Applications of Artificial Intelligence are also considered.
Editorial Process
From the time a paper is received to the time a final decision is made, the workflow associated with each paper is explained below including submission instructions.
Before Submission
Authors should read this document to familiarize themselves with the expectations of the journal. The author submitting a manuscript is expected to have an account on IEEE Author Portal https://ieee.atyponrex.com/journal/tai-ieee
Editorial Assistant Compliance and Plagiarism Checking
A submitted paper is first checked with the Editorial Assistant to ensure
- There is no corrupted file during the loading of the paper
- Double-anonymized
- Appropriate Formatting
- Compliance with page limit
- Compliance with Ethics for papers involving human and/or animal experiments
A manuscript that fails any of the above, will be returned to authors.
If the manuscript passes the first checklist above, the Editorial Assistant will run a plagiarism report. The maximum allowable similarity index for a manuscript is 20% assuming that statements are quoted and cited. Manuscripts that exceed this threshold will receive a straight reject.
Editor in Chief
The Editor in Chief may reject a manuscript without sending it for review if:
- The author(s) have not followed the IEEE guidelines for style.
- The author(s) have violated IEEE Policies.
- The manuscript is incomprehensible (in other words, so poorly written that it is unreadable).
- The subject and contents of the article do not meet the scope of the periodical or a specific special issue, or the abstract, introduction and/or conclusion are inaccessible to the journal’s wide readership pool.
- The manuscript raises ethical concerns for manuscripts involving human and/or animal participation.
- The manuscript does not meet the very minumum techncal grounds for the journal.
If a manuscript passes the above, the Editor in Chief will assign an appropriate Associate Editor to handle the manuscript.
Associate Editor
Manuscripts will be assigned 3-4 reviewers. Decisions can be made on manuscripts based on two reviews only if and when the Associate Editor sees this appropriate. For example, the Associate Editor can opt to make a decision on a manuscript with two rejects without waiting for additional reviews.
Reviewers
Reviewers are technical experts in the field of the manuscript. TAI aims to provide constructive reviews. TAI expects reviewers to be professional and impartial in their judgement. In some circumstances, a manuscript may get sent to a reviewer who is expert in the wider technical area of a manuscript, without necessarily be an expert in the narrow technical area of the manuscript. This is an example where it is vital for the manuscript to be written in a language to make it accessible to a wider audience.
In addition to providing a written report on each manuscript, reviewers are required to answer a few questions:
- How would you describe the quality of technical writing used in this manuscript?
- How would you describe the quality of English used in this manuscript?
- Are the abstract, introduction, and conclusion written in an accessible language to a non-specialist?
- Is the work reproducible?
- How novel is the contribution?
- How significant is the contribution?
- Should this manuscript be considered for a 'Best Paper' award?
Some reviewers prefer to load their written report as a file that will be available to authors through Manuscript Central.
Reviews could be resent back to reviewers by the Associate Editor if:
- The review appears too shallow
- The comments do not match the decision proposed by the reviewer
- The review is not objective and/or uses inappropriate language
Decisions on Manuscripts
After reviewers return their reviews with recommendations, the Associate Editor handling the manuscript will write a meta review with a recommendation. The Editor in Chief will make the final decision on the manuscript, which will then be communicated to authors.
Revisions
Manuscripts with a Minor Revision decision will be allowed 15 days to resubmit their revised manuscript. Manuscripts with a Major Revision decision will be allowed 30 days to resubmit their revised manuscript. Revised manuscripts that are received after these timeframes will need to be submitted as new manuscripts. ScholarOne Manuscripts Central will indicate to authors the number of days left before a deadline passes.
Appeal Process
Authors who wish to appeal a decision, they must submit their appeal in writing to the Editor-in-Chief within 30 days of the decision they appeal. The Editor-in-Chief will make a decision on the appeal within 15 days. Authors should discuss with the Editor-in-Chief if they are still unhappy with the decision on appeal and can escalate the appeal to the IEEE CIS VP Pubs if the discussion with the Editor-in-Chief is unsatisfactory.
Expecteed Time for Review
We aim to provide speedy decisions on submissions. Associate Editors are requested to handle papers while aiming for a decision within seven weeeks. Our average weeks from submission to first decision sits around 12 weeks mark. However, each submission is unique and may take a different amount of time to review; therefore, outliers exist, unfortunately. The editorial assistant and Editor-in-Chief do their best to follow up with reviewers and Associate Editors.
IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence 2024 Editorial Board
Editor-in-Chief

IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence Founding Editor-in-Chief
University of New South Wales - Canberra
Associate Editors
|
Name |
Affilation |
Country/Region |
| Zahid Akhtar | State University of New York Polytechnic Institute | USA |
| Aparna Akula | Central Scientific Instruments Organisation | India |
| Plamen Angelov | Lancaster University | UK |
| Sansanee Auephanwiriyakul | Chiang Mai University | Thailand |
| Mehala Balamurali | University of Sydney | Australia |
| Sanghamitra Bandyopadhyay | Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata | India |
| Tanvi Banerjee | Wright State University | USA |
| Aaron Baughman | IBM | USA |
| Olfa Belkahla Driss | Ecole Supérieure de Commerce de Tunis | Tunisia |
| Mohammed Bennamoun | University of Western Australia | Australia |
| Anastasios Bezerianos | Information Technologies Institute | Greece |
| Ying Bi | Zhengzhou University | China |
| Hamid Bouchachia | Bournemouth University | UK |
| João Catalão | University of Porto, Portugal | Portugal |
| C.L. Philip Chen | Macau University | China |
| Shyi-Ming Chen | National Taiwan University of Science and Technology | Taiwan |
| Ran Cheng | Southern University of Science and Technology | China |
| Fahmida Chowdhury | National Science Foundation | USA |
| Pau-Choo Chung | National Cheng Kung University | Taiwan |
| Oscar Cordón | University of Granada | Spain |
| Keeley Crockett | Manchester Metropolitan University | UK |
| Dipankar Dasgupta | The University of Memphis | USA |
| Guilherme DeSouza | University of Missouri | USA |
| Weiping Ding | Nantong University | China |
| Yucheng Dong | Sichuan University | Taiwan |
| Yali Du | King's College London | India |
| Pierpaolo D'Urso | University of Rome | Italy |
| Mehmet Efe | Hacettepe University | Türkiye |
| Mohammed El-Abd | American University of Kuwait | Kuwait |
| Pablo Estevez | University of Chile | Chile |
| Ali Etemad | Queen’s University | Canada |
| Giancarlo Fortino | University of Calabria | Italy |
| Alejandro Frangi | University of Manchester | UK |
| Huazhu Fu | Agency for Science, Technology and Research | Singapore |
| GANGADHARAN G R | NIT Tiruchirappalli, INDIA | India |
| Chiara Gallese | University of Turin | Italy |
| Matthew Garratt | University of New South Wales | Australia |
| Alexander Gegov | University of Portsmouth | UK |
| Hani Hagras | University of Essex | UK |
| Zahid Halim | Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology | Pakistan |
| Ibrahim Hameed | Norwegian University of Science and Technology | Norway |
| Haibo He | University of Rhode Island | USA |
| Sean Holden | University of Cambridge | UK |
| Sameera Horawalavithana | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory | USA |
| Xiao-Min Hu | Guangdong University of Technology | China |
| Yo-Ping Huang | National Taipei University of Technology | Singapore |
| Tingwen Huang | Texas A&M University at Qatar | Qatar |
| Robert Hunjet | Defence Science and Technology Group | Australia |
| Amir Hussain | Napier University | UK |
| Omar Hussain | UNSW Canberra | Australia |
| Aya Hussein | University of Canberra | Australia |
| Alexandros Iosifidis | Aarhus University | Denmark |
| Yumi Iwashita | NASA JPL | China |
| Chaker Abdelaziz Kerrache | University of Laghouat | Algeria |
| Deepika Koundal | University of Petroleum & Energy Studies | India |
| Neeraj Kumar | Thapar University Patiala Punjab | India |
| Albert Lam | Fano Labs | Hong Kong |
| Douglas Lange | Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center Pacific | USA |
| Annabel Latham | Manchester Metropolitan University | UK |
| Boaz Lerner | Ben-Gurion University of the Negev | Israel |
| Junhua Li | University of Essex | UK |
| Qing LI | Hong Kong Polytechnic University | Hong Kong |
| Xiang Li | Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School | USA |
| Xiaoli Li | Agency for Science, Technology and Research | Singapore |
| Kaitai Liang | TU Delft | The Netherlands |
| Joo-Hwee Lim | Agency for Science, Technology and Research | Singapore |
| Chin Teng Lin | University of Technology Sydney | Australia |
| Jialin Liu | Southern University of Science and Technology | China |
| Lin Liu | University of South Australia | Australia |
| Qingwen Liu | Tongji University | China |
| Qinghua Lu | CSIRO | Australia |
| Hao Luo | Harbin Institute of Technology | China |
| Dwarikanath Mahapatra | Inception Institute of Artificial Intelligence | UAE |
| Letizia Marchegiani | University of Parma | Italy |
| Panagiotis (Panos P.) Markopoulos | The University of Texas at San Antonio | USA |
| Yi Mei | Victoria University of Wellington | New Zealand |
| Supratik Mukhopadhyay | Louisiana State University | USA |
| Anand Nayyar | Duy Tan University | Viet Nam |
| Hung Nguyen | The University of Adelaide | Australia |
| Geoff Nitschke | University of Cape Town | South Africa |
| Ben Niu | Shenzhen University | China |
| Marco Nobile | Ca' Foscari University of Venice | Italy |
| Gustavo Olague | CICESE | Mexico |
| Diego Oliva | Universidad de Guadalajara | Mexico |
| Yew Soon Ong | Nanyang Technological University | UK |
| Karen Panetta | Tufts Univeristy | USA |
| Alvaro Parra | Seeing Machines | Australia |
| Anand Paul | Kyungpook National University | South Korea |
| Francesco Piccialli | University of Naples Federico II | Italy |
| Mihail Popescu | University of Missouri | USA |
| Paolo Remagnino | Durham University | UK |
| Manuel Roveri | Politecnico di Milano | Italy |
| Melike Sah Direkoglu | Near East University | Cyprus |
| Monjoy Saha | National Cancer Institute | USA |
| Sriparna Saha | Indian Institute of Technology Patna , India | India |
| KC Santosh | University of South Dakota | USA |
| Teena Sharma | The University of Tennessee | India |
| Chao Shen | Xi'an Jiaotong University | China |
| Peng Shi | Adelaide University | Australia |
| Houbing Song | Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University | USA |
| Peter Stuckey | Monash | Australia |
| Xiaojie Su | Chongqing University | China |
| Koduvayur Subbalakshmi | Stevens Institute | USA |
| Chaoli Sun | Taiyuan University of Science and Technology | China |
| Johan Suykens | Katholieke Universiteit Leuven | Belgium |
| KC Tan | City University of Hong Kong | Hong Kong |
| Jim Torresen | University of Oslo | Norway |
| Ivor Tsang | Agency for Science, Technology and Research | Singapore |
| kanishka Tyagi | Aptiv Advance Research Center | USA |
| Kyriakos Vamvoudakis | Georgia Institute of Technology | USA |
| Thanos Vasilakos | University of Agder | Norway |
| Alvaro Velasquez | DARPA | USA |
| Marley Vellasco | Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio de Janeiro | Brazil |
| Nishchal Verma | Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur | India |
| Vincenzina Vitale | Sapienza University of Rome | Italy |
| Christian Wagner | University of Nottingham | UK |
| Min Wang | University of Canberra | Australia |
| Xiao Wang | Beihang University | China |
| Qinglai Wei | Chinese Academy of Sciences | China |
| Michael Wooldridge | Oxford | UK |
| Feng Xia | RMIT University | Australia |
| Bing Xue | Victoria University of Wellington | New Zealand |
| Simon Yang | University of Guelph | Canada |
| Lina Yao | CSIRO | Australia |
| Xin Yao | Southern University of Science and Technology | China |
| Gary Yen | Oklahoma State University | USA |
| Zhi-Hui Zhan | South China University of Technology | USA |
| Jingfeng Zhang | RIKEN | Japan |
| Jun Zhang | Hanyang University | Hong Kong |
| Dongbin Zhao | University of Chinese Academy of Sciences | China |
| Jia Zhu | Zhejiang Normal University | China |
Updated: 3/11/24
Information for Authors
IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence Author Instructions
Note: IEEE TAI has switched to Double Anonymous Review Policy. Authors must exclude any author-identifying information in their PDF files.
Paper Template
https://template-selector.ieee.org/
Submission Site
https://ieee.atyponrex.com/journal/tai-ieee
Aims & Scope
The IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (TAI) is a multidisciplinary journal publishing papers on theories and methodologies of Artificial Intelligence. Applications of Artificial Intelligence are also considered. The aim is to publish impactful research in Artificial Intelligence, survey articles, and applications.
Types of Contributions
IEEE TAI publishes three types of articles:
Original Research Regular Manuscripts
Original Research Regular Manuscripts represent significant contributions with novel experimental, analytical, and/or theoretical findings. These articles could be application focused, where the novelty lies in the methodology for adopting an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to a challenging application. The work needs to be self-contained, scientifically sound, evidence-based, and representing a conclusive treatment of a problem.
Original Research Review Manuscripts
Original Research Review Manuscripts offer a systematic survey and a critical assessment of a scientific field with an aim to synthesize the research already done by others into a new form. A review article needs to articulate the methodology for the review including the inclusion and exclusion criteria (methodological filter) for the papers being reviewed. The synthesis should lead to open research questions addressing significant research gaps and/or new conceptual frameworks.
Original Research Briefs Manuscripts
Original Research Briefs Manuscripts are shorter forms of research articles. They could offer sufficiently interesting new theoretical, experimental, and/or analytical findings, short comments on topical issues of interest to the journal readership, and/or a blue-sky idea with appropriate evidence of the potential of the idea and its impact on artificial intelligence.
Manuscript Category Responsibilities
During the review process, submitted manuscripts will NOT be transferred from one category to another after submission/review. It is the responsibility of authors to decide the category of their manuscript at the time of submission. The articles in this journal are peer reviewed in accordance with the requirements set forth in the IEEE Publication Services and Products Board Operations Manual (https://pspb.ieee.org/images/.les/.les/opsmanual.pdf). Each published article was reviewed by a minimum of two independent reviewers using a single-blind peer review process, where the identities of the reviewers are not known to the authors, but the reviewers know the identities of the authors.
Restrictions to Notice
|
Paper Type |
Normal Page Limit |
Extra Page Limit |
Max total |
|
Original Research Regular Manuscripts |
10 |
5** |
15 |
|
Original Research Review Manuscripts |
15 |
6** |
21 |
|
Original Research Brief Manuscripts |
6 |
3** |
9 |
- Maximum number of words in the title 15 words
- Maximum length of running head 25 characters
- Maximum length of abstract 250 words
- Minimum number of keywords 3
- Maximum number of keywords 6
** Current mandatory page charges are US$200 per extra page.
Open Access
This publication is a hybrid journal, allowing either Traditional manuscript submission or Open Access (author-pays OA) manuscript submission. Upon submission, if you choose to have your manuscript be an Open Access article, you commit to pay the discounted $2,045 OA fee if your manuscript is accepted for publication in order to enable unrestricted public access. Any other application charges (such as over-length page charge and/or charge for the use of color in the print format) will be billed separately once the manuscript formatting is complete but prior to the publication. If you would like your manuscript to be a Traditional submission, your article will be available to qualified subscribers and purchasers via IEEE Xplore. No OA payment is required for Traditional submission.
Open access is provided through the payment of an article processing charge (APC) paid after acceptance. APCs are often financed by an author's institution or the funder supporting their research.
Corresponding authors from low income countries are eligible for waived or reduced APCs.
Double-Anonymous Review
The articles in this journal are peer reviewed in accordance with the requirements set forth in the IEEE PSPB Operations Manual (sections 8.2.1.C & 8.2.2.A). Each published article was reviewed by a minimum of two independent reviewers using a double-anonymous peer review process, where the identities of the reviewers are not known to the authors, and the reviewers are not provideed with the identities of the authors at the time of review. Articles will be screened for plagiarism before acceptance.
IEEE Guidelines on AI-Generated Text
The use of artificial intelligence (AI)–generated text in an article shall be disclosed in the acknowledgements section of any paper submitted to an IEEE Conference or Periodical. The sections of the paper that use AI-generated text shall have a citation to the AI system used to generate the text.
Ethics
All IEEE authors are expected to adhere to IEEE’s publishing ethics, including the definition of authorship, the appropriate citation of sources, the accurate reporting of data, and the publishing of original research. Visit the IEEE Author Center to learn more. All articles submitted for publication should be original and not under consideration elsewhere; if your article is based on a previous publication such as a conference proceeding, cite the original publication and clearly indicate how the articles differ.
Papers involving human or animal participation must include in their manuscript information on the ethics clearance protocol followed and the approval number from an appropriate ethics committee.
Contact the Editor-in-Chief with any questions on publishing ethics.
Extending Conference Papers
The journal accepts an extended version of authors' conference papers with the following conditions:
- The submitted journal version of the paper contains additional substantial contributions to the conference version. Examples of substantial contributions include significant methodological improvements, essential mathematical proofs, or significant extension to experimental frameworks. The mere addition of experiments on new datasets or expanding the background section, while important, are not considered substantial contributions.
- Authors must reference the conference paper, explain the difference, and list the additional contributions.
- Similarity index does not exceed 25% excluding bibliography and preprints of the same paper.
Manuscript Organization
The IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence (TAI) aims to reach out to a wide readership pool that includes academics, practitioners, executives, and policy makers. The journal presents technical contents requiring technical rigor and, correct and sound investigations.
To respect the double-anonymized review policy, authors should exclude their names, contact information, and affiliations from the entire manuscript including frontmatter information, figures, tables, acknowledgement, references, supplementary materials, and links to external websites such as GitHub. To refer to their prior work, authors should use a third-person voice. For example, instead of writing “Our prior work (Mary and Michael, 2023) has shown”, you can write “Mary and Michael (2023) have shown” or “The work of Mary and Michael (2023) has shown”. Exclude acknowledgements and any references to funding sources. These information are provided in author portals.
A manuscript in TAI needs be structured well to achieve these objectives. It is recommended that authors adhere to the following guidelines when organizing their manuscript.
- Title
- Abstract
- Impact Statement
- Introduction
- Background
- Methodology
- Theory/Analysis, Experimental Design/Results/Analysis/Discussion
- Conclusion and Future Work
- References
- Supplementary Materials if any
The title should be concise and reflect the scope, contribution(s) and significance of the work.
Avoid phrases such as “a novel methodology”, “a new algorithm”, and “a significant application” in the title. By default, papers in TAI offer novel contributions that are significant. One purpose of the paper is to convince the reader that the contribution is novel, scientifically sound, technically correct, and significant. As such, words such as ‘novel’ and ‘new’ are redundant.
The “Abstract”, “Introduction” and “Conclusion and Future Work” sections must be accessible to the wide readership of TAI. A non-specialist needs to be able to understand the problem the manuscript is attempting to solve, the motivation and significance of the problem, the novelty of the proposed solution and how it advances the field, the significance of the findings, and the remaining research questions that other researchers could use to continue with a similar line of work.
The “Abstract” should not exceed 250 words. Authors are encouraged to attempt to use the following guideline in writing their abstract:
- 1 to 2 sentences introducing the problem.
- 2 to 3 sentences summarizing the state-of-art. Be concise and offer an objective assessment of the current state of play in this area.
- 1 to 2 sentences clearly describing the research gap the paper is concerned with.
- 1 to 2 sentences summarizing the main methodological contribution.
- 1 to 2 sentences summarizing the main result.
- 2 to 3 sentences summarizing the implications of the findings on the wider field of AI.
The introduction should motivate the work, expand on the problem definition and discusses an initial summary of the state of the art with the absolute minimum use of technical jargon.
For mathematically oriented manuscripts, over-use of mathematics should be avoided. The purpose of mathematics is to be concise, formalize the problem, and support the technical soundness of the contribution. Mathematical proofs should be complemented with explanations sufficient for a graduate student to follow the logic of the proof. Obvious steps in a proof that get skipped by an expert should be included in the supplementary materials for a graduate student to follow the proofs.
For experimental manuscripts, authors should adhere to the scientific method. A clear hypothesis needs to be established. Experimental validity should guide the experimental design. Appropriate statistical tests of significance should be used before making any claim on the superior performance of one algorithm over another. Claims should be scientifically sound, driven from the analysis, and should not exaggerate the findings. When comparing a proposed algorithm to others from the literature, the paper should avoid excessive comparisons. It is sufficient to compare against the top two or three most recent and competitive algorithms in the field of the paper. The choice of these algorithms should be justified.
For survey manuscripts, there should be a clear and systematic survey methodology. Previous survey papers in the area should be acknowledged and summarized before updating the survey with new advances in the field. A survey paper needs to synthesize the literature into a new form such as a conceptual model and/or open research questions.
Each paper should have a conclusion and future work section. The conclusion should summarize the key finding of the paper and position it in the wider research area. Future research directions stemming from a paper’s findings need to be discussed in a concise manner. Authors are encouraged to avoid superficial and very generic future research statements.
References should cover recent papers. Unless the manuscript is addressing a long-forgotten topic in artificial intelligence, it is expected that the majority of references will be dedicated to recent publications. Self-reference should be kept to the absolute minimum necessary.
The Impact Statement:
It is becoming more important than ever that the science published in top tier journals such as the IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, needs to be communicated widely to the community and readership of the journal.
Every good piece of research has an impact, but it could become deeply hidden in the technical language used to describe the work, making it harder for non-specialists to understand it. To facilitate making the wider readership pool of the journal to understand the research published in the Transactions, each paper must include a 100-150 words impact statement following the abstract.
The statement needs to offer a concise explanation of the impact of the research and findings. Authors may wish to be guided by the PESTEL dimensions: political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal. Explain how the manuscript substantially advances the knowledge base in the specific branch of AI and the wider field of AI, and the ‘so-what’ question by reflecting on how the findings could be beneficial for some or all of the PESTEL dimensions.
Impact statements are taken seriously in the evaluation of the manuscript and its suitability for IEEE TAI. The impact statement should convince a smart, but not necessarily a specialist, reader that your work is novel and will create a legacy in the research area. Your paper may get returned to you without review if the impact statement is thin, ambiguous, a copy of the abstract, or does not demonstrate a real advance in the scientific or technological field that matters.
A YouTube video explaining how to write an Impact Statement by the Founding Editor-in-Chief can be viewed by Clicking Here.
Tips for writing good impact statements:
Do not repeat the abstract. The abstract is about the what, why, how and findings. The impact statement is about the ‘so-what’.
Please avoid ambiguous statements, exaggeration or under-estimation of impact, and technical jargons.
A journalist or a politician with no expertise in AI should be able to read your impact statement and understand the significance of the research.
Authors may wish to read https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/731328
Hypothetical Example 1 of an impact statement:
Chatbots are a popular technology in online interaction. They reduce the load on human support teams and offer continuous 24-7 support to customers. However, recent usability research has demonstrated that 30% of customers are unhappy with current chatbots due to their poor conversational skills and inability to emotionally engage customers. The natural language algorithms we introduce in this paper overcome these limitations. With a significant increase in user satisfaction to 92% after adopting our algorithms, the technology is ready to support users in a wide variety of applications including government front-shops, automatic tellers, and the gaming industry. Moreover, the proposed technology could offer an alternative way of interaction for some physically disable users.
Hypothetical Example 2 of an impact statement:
While existing pattern recognition algorithms in autonomous cars can detect 99% of obstacles during a clear day, their accuracy drops to 10% in low-visibility environments with fog or heavy rain. The technology proposed in this paper has improved the accuracy of these algorithms in low-visibility environments to 80%. This improvement caused the expected number of collisions for autonomous cars to fall below the safety threshold needed to deploy them on roads. The economic implication of this advance is expected to increase GDP with 5% over the next five years, while reducing death tolls in the streets to less than 45% of current figures.
Article Submission
- All articles must be submitted via our submission site at https://ieee.atyponrex.com/journal/tai-ieee
- Format your article for submission by using the standard IEEE two column format. Style files are available from the IEEE Author Center. In particular, please use the Latex template available here.
- Submit your article text in two-column PDF IEEE format. Visit the IEEE Author Center for information on writing the abstract, using equations in your article, publishing author names in native languages, and more.
- Authors will need to submit a minimum of three and a maximum of six keywords chosen from a dropdown list. These keywords are important to identify and assign appropriate reviewers to the manuscript. Authors need to choose the keywords that match their manuscript. If none of the keywords exactly match the manuscript, authors need to select the closest keywords from the list that match their manuscript. If there are absolutely no keywords that match the manuscript, the authors need to rethink of the relevance of their manuscript to IEEE TAI.
- Submit your figures individually in PS, EPS, PDF, PNG, or TIF format. Visit the IEEE Author Center for information on resolution, size requirements, file naming conventions, and more.
- For information on submitting supplementary material such as graphical abstracts, multimedia, or datasets, visit the IEEE Author Center.
- A rejected paper should not normally be submitted again to the journal. If it has gone significant and substantial changes to contents to eliminate all issues identified in the rejection letter, authors could consult with the Editor-in-Chief to check if their paper has changed in form and contents sufficiently to warrant a new submission. This piece of guideline is to avoid repeated desk reject decisions when rejected papers cycle back with similar forms and contents; overloading the review system of the journal.
ORCID
All IEEE journals require an Open Researcher and Contributor ID (ORCID) for all authors. ORCID is a persistent unique identifier for researchers and functions similarly to an article’s Digital Object Identifier (DOI). You will need a registered ORCID to submit an article or review a proof in this journal. Learn more about ORCID and sign up for an ORCID today.
English Language Editing Services
English language editing services can help refine the language of your article and reduce the risk of rejection without review. IEEE authors are eligible for discounts at several language editing services; visit the IEEE Author Center to learn more. Please note these services are fee-based and do not guarantee acceptance.
Share Your Code and Data
Increase the impact of your work by sharing your code and data for others to view, build upon, and reuse. IEEE works with Code Ocean [https://codeocean.com/], a cloud-based computational reproducibility platform, to make your code discoverable. IEEE DataPort [https://ieee-dataport.org/], an online data repository of datasets and data analysis tools, makes your datasets discoverable. Visit the IEEE Author Center for more information.
IEEE Author Tools
Preparing your article for submission is easy with IEEE Author Tools. Tools are available to help you find the right publication for your research, check the quality of your graphics, validate your LaTeX files, and verify your reference list.
Page Charges
After a manuscript has been accepted for publication, the author’s company or institution will be requested to pay a charge of $110 per printed page to cover part of the cost of publication. Page charges for this transaction, like those for journals of other professional societies, are not obligatory nor is their payment a prerequisite for publication. Articles submitted to this transaction will be imposed a mandatory over-length page charge for pages in excess of 10 pages for a regular paper, 15 pages for a review paper, 6 pages for a brief paper, 10 pages for an invited paper, and 15 pages for an invited review paper. Authors of articles accepted for publication will be assessed a mandatory page charge of $200 (per page) for every printed page over these limits.
Post-Acceptance
If your article is accepted for publication, you will receive emailed instructions regarding your next steps. You may be asked to upload final production-ready files. Shortly after final files are uploaded, you will receive your article proofs for final review, along with instructions on how to review your proofs and submit any corrections. Please note that major changes to your article, including the list of references, are not permitted after the article is accepted for publication. Please contact the Editor-in-Chief if you have any doubts about whether a modification you wish to make is appropriate.
Copyright
It is the policy of the IEEE to own the copyright of the technical contributions it publishes. IEEE has moved to an all-electronic copyright submission system. Once you have submitted your final files you will be automatically redirected to the IEEE electronic copyright form where you will be able to complete copyright transfer or select an appropriate license agreement. Hard copy copyright forms are no longer acceptable.
Author Names in Native Languages
IEEE supports the publication of author names in their native language alongside the English versions of their names in the author list of an article. For more information, please visit the IEEE Author Center at the following URL: https://journals.ieeeauthorcenter.ieee.org/create-your-ieee-article/create-the-text-of-your-article/publishing-author-names-in-native-languages/.
IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence

Welcome to the page for the IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence (IEEE TAI). IEEE has established the new journal our community has been waiting for to publish our work on Artificial Intelligence! The submission site for manuscripts accepts submissions to the journal. Don’t miss out on this opportunity and join the community of authors who are publishing in the IEEE TAI! It is time to prepare your best piece of work for IEEE TAI to increase your visibility in the international AI community and to be among the top authors to publish in IEEE TAI.
Queries to the Founding Editor-in-Chief, Prof. Hussein Abbass from UNSW Canberra, Australia, at ieee.tai.eic@gmail.com.
Scope
The IEEE Transactions on artificial intelligence (TAI) is a multidisciplinary journal publishing papers on theories and methodologies of Artificial Intelligence. Applications of Artificial Intelligence are also considered.
A video with example publications can be seen [Here]
Impact Score
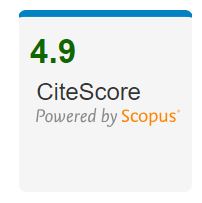
The values displayed for the journal bibliometrics fields in IEEE Xplore are based on the Journal Citation Report from Clarivate from the 2022 report released in June 2023. Journal Citation Metrics Journal Citation Metrics such as Impact Factor, Eigenfactor Score™ and Article Influence Score™ are available where applicable. Each year, Journal Citation Reports© (JCR) from Thomson Reuters examines the influence and impact of scholarly research journals. JCR reveals the relationship between citing and cited journals, offering a systematic, objective means to evaluate the world's leading journals. Find out more about IEEE Journal Rankings.
IEEE Guidelines on AI-Generated Text
The use of artificial intelligence (AI)–generated text in an article shall be disclosed in the acknowledgements section of any paper submitted to an IEEE Conference or Periodical. The sections of the paper that use AI-generated text shall have a citation to the AI system used to generate the text.
Paper template can be accessed here.
Sponsors




